When levels of uric acid, a naturally occurring waste product in the body, rise above normal, this painless chemical can become a dangerous threat. Gout, a famously painful kind of arthritis, is mostly caused by this change. In this article, we will examine the subtleties of gout development, identify the causes of high uric acid levels, and examine the best ways to control and lower this bothersome substance. Read on to learn helpful tips and doable remedies for a pain-free life if you are looking for gout relief or just want to maintain healthy uric acid levels.
Signs and Symptoms
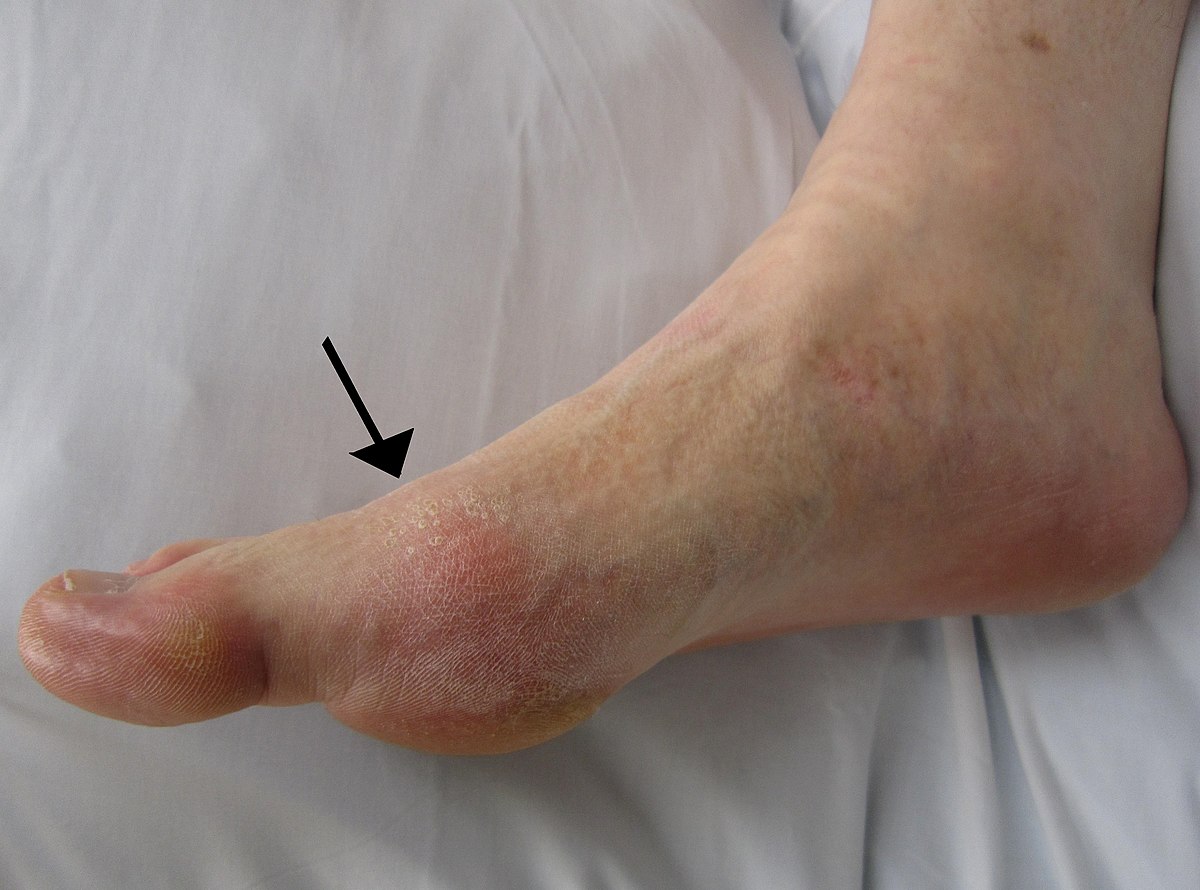
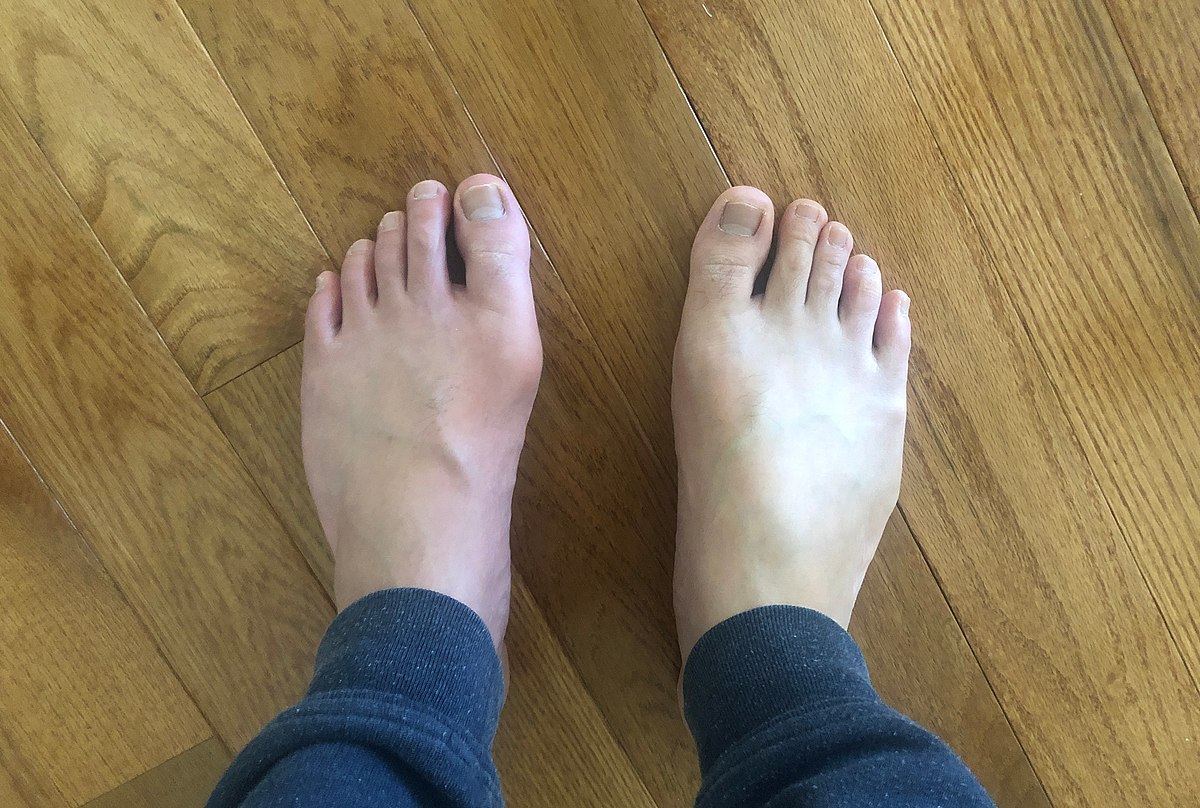
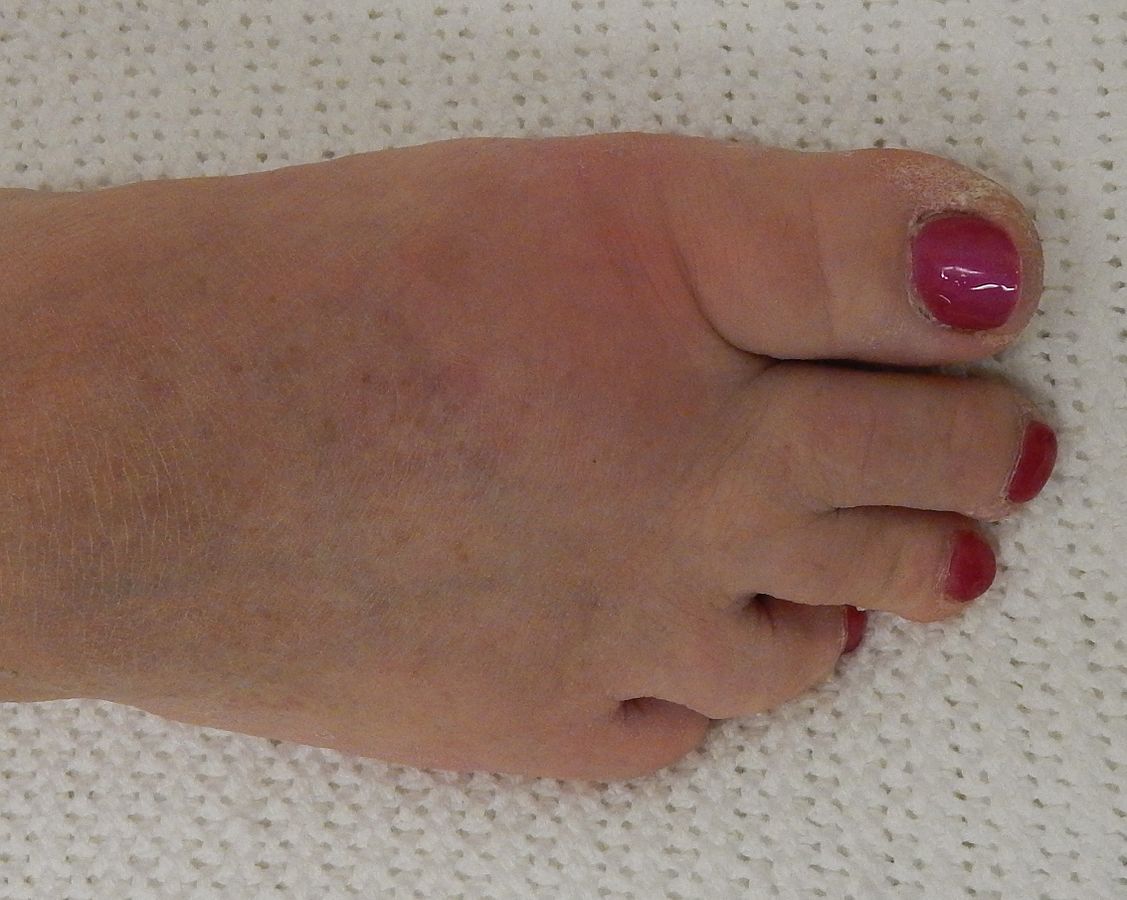
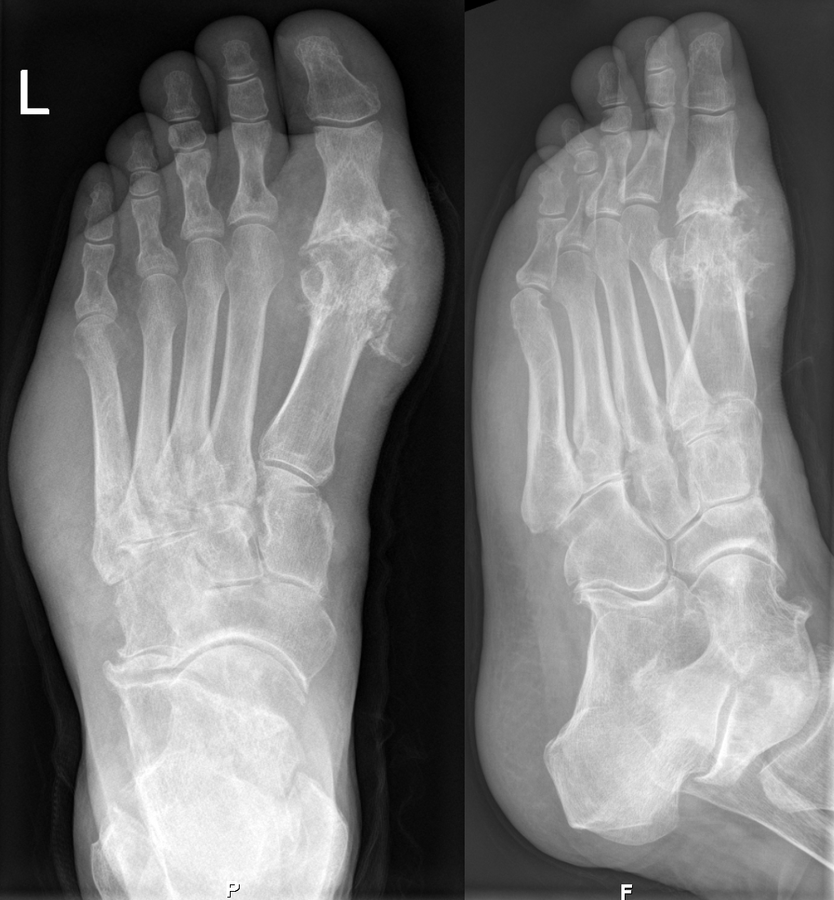
Although gout can appear in a variety of ways, the most typical symptom is recurring acute inflammatory arthritis, which causes a red, sensitive, hot, and swollen joint. The big toe’s metatarsophalangeal joint, which accounts for half of cases, is most frequently afflicted. Other joints, including the heels, knees, wrists, and fingers, may also be impacted. Joint discomfort often starts at night and peaks 24 hours after commencement. The major cause of this is a decreased body temperature. Rarely, other symptoms like weariness and a high temperature may also appear along with the joint discomfort.
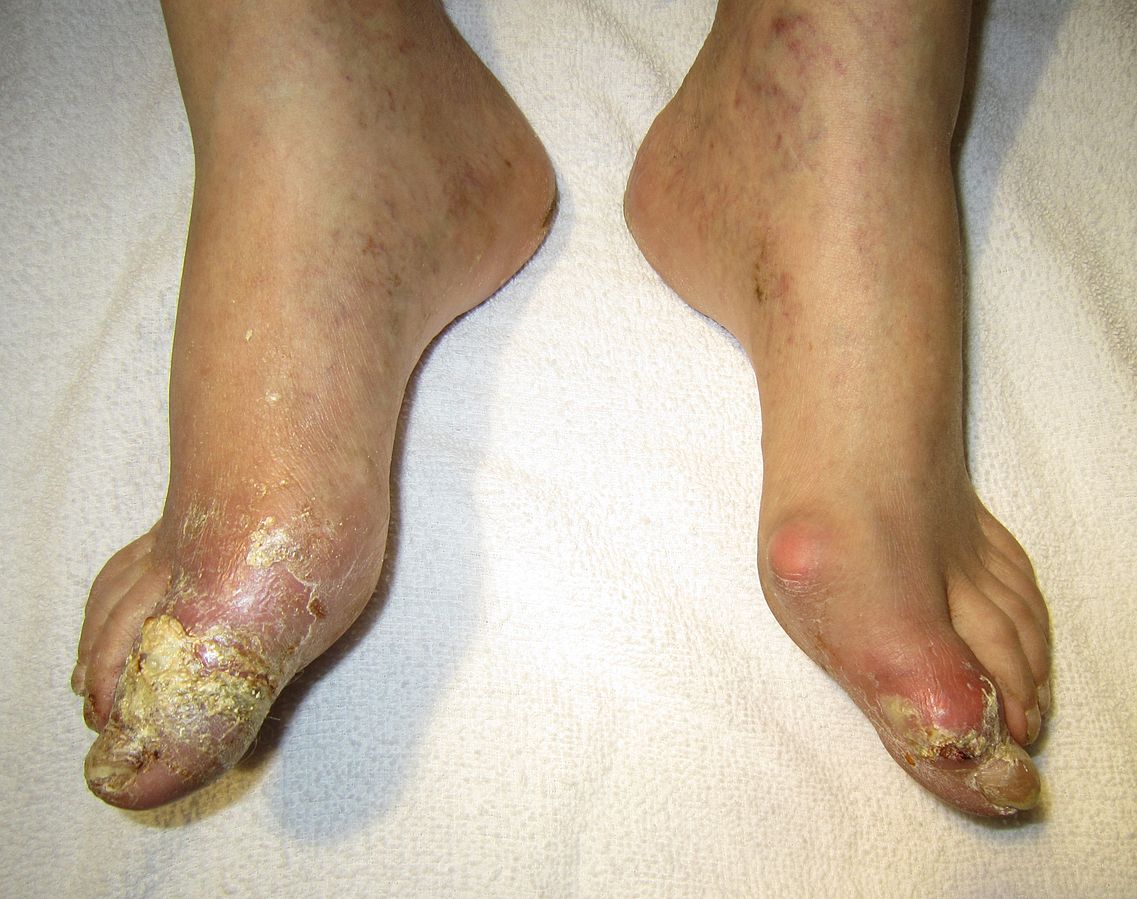
Hyperuricemia, or persistently high levels of uric acid, can cause a variety of symptoms, including tophi, which are tophi are hard, painless deposits of uric acid crystals. Due to bone degradation, extensive tophi may cause persistent arthritis. Acute uric acid nephropathy and kidney stones can both develop as a result of elevated uric acid levels precipitating crystals in the kidneys.
What Causes Gout?
Purines, which are organic substances present in every cell of your body and many meals, notably red meat, organ meats, certain shellfish, sugary drinks, and beer, are broken down into uric acid by some people who have high amounts of uric acid.
Uric acid can accumulate in the body and form needle-like crystals that lodge in joints, producing sudden, intense pain and swelling. This can happen either because the kidneys are not excreting it as much as they should or because you are eating too much uric acid from a high-purine diet.
Whether or not they are treated, gout episodes often reach their climax after 12 to 24 hours and then gradually subside on their own. You could just experience one gout episode in your entire life or a few. Untreated recurrent gout episodes may eventually include more joints, continue longer, and become more severe. Some people ultimately develop tophi, which are large collections of uric acid crystals that can take the shape of hard lumps in the soft tissues or the bones near joints.
Risk Factors
You have a higher risk of getting gout if you:
- Consume a lot of foods high in purines, such as red meat and various varieties of seafood, particularly scallops, sardines, and tuna, but the health advantages of doing so likely outweigh any potential gout risks
- Consume large amounts of alcohol, particularly beer, or consume foods and beverages containing high-fructose corn syrup as its sweetener
- Overweight, which makes it difficult for your body to eliminate uric acid and causes it to create more of it
- Have gout in your family
- Have a chronic illness, such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, or renal disease
- Take medications for high blood pressure, such as beta blockers and diuretics
- The billions of bacteria, viruses, and fungus that inhabit your gut and control your immune system, are out of balance. The majority of inflammatory disorders, including arthritis, are linked to the microbiome
Diagnosing Gout
Gout may be diagnosed using your medical history, a physical examination, and testing. Your doctor will also want to rule out any other conditions like an infection, trauma, or another form of arthritis that might be causing your joint pain and inflammation. You could have tests like:
- Analysis of joint fluids. The best method for gout diagnosis is this. Your doctor removes fluid from the painful joint(s) and looks for uric acid crystals there under a microscope.
- Test for uric acid in the blood. On the other hand, some persons with gout have normal uric acid levels, while many people with high blood uric acid levels never acquire gout.
- Uric acid crystals in joints can be seen with imaging techniques including X-rays, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, and dual-energy computer tomography.
How to decrease uric acid naturally
Limit purine-rich foods
Purines are substances that are found in some foods naturally. Uralic acid is created by the body as it breaks down purines. Too much uric acid is produced during the digestion of purine-rich meals, which can result in gout.
Some generally healthy foods have high purine content; thus it may be preferable to restrict intake rather than completely avoid them.
Among the foods high in purine are:
- Wild game, such as meat from deer
- Fish such as herring, trout, tuna, haddock, sardines, and anchovies are also common
- Alcohol in excess, including beer and liquor
- Meals with a lot of fat, like bacon, dairy, and red meat, including veal
- Organ meats like sweetbreads and liver
- Sweet meals and drinks
Among the foods having a modest purine concentration are:
- Deli meats
- Ham and beef, among the majority of other meats
- Poultry
- Lobster, oyster, shrimp, and crab
Eat more meals low in purine
While some meals contain a lot of purines, others do not. They may be incorporated into a person’s diet to assist in lowering uric acid levels. The following list of foods contains little purine:
- Dairy products with reduced or no fat
- Most nuts and peanut butter
- Most veggies and fruits
- Coffee
- Whole-grain bread, potatoes, and rice
Although dietary adjustments alone will not cure gout, they could help stop flare-ups. It is also crucial to remember that not everyone who develops gout consumes a diet heavy in purines.
Avoid using medicines that cause uric acid to rise
Uric acid levels may rise as a result of several drugs. These consist of:
- Such as furosemide (Lasix) and hydrochlorothiazide, are diuretic medications
- Medications that lower immunity, particularly before or after organ transplants
- Doses of aspirin
Although uric acid-raising drugs may provide important health advantages, patients should see a doctor before quitting or switching any medications.
Keep your body at a healthy weight
As obesity raises the risk of gout, maintaining a reasonable body weight may help lower the risk of gout flares.
Experts advise people to concentrate on making long-term, sustainable adjustments to manage their weight, such as increasing their activity level, eating a balanced diet, and selecting foods that are high in nutrients. Lowering blood uric acid levels and enhancing general health can both be accomplished by maintaining a healthy weight.
Make use of a vitamin C supplement
Blood uric acid levels and vitamin C consumption are positively correlated. While pointing out this result, there was no definitive proof that vitamin C can prevent or lessen gout episodes.
Avoid alcoholic and sweetened beverages
A higher risk of getting gout is linked to heavy alcohol and sugary beverage use, such as sodas and sweetened juices.
Alcohol and sweetened beverages also provide extra calories to the diet, which may result in weight gain and metabolic problems that raise uric acid levels.
Drink coffee
Coffee drinkers are less likely to acquire gout. There may be an association between consuming coffee and a decreased risk of gout. However, there was not enough proof to support a definitive relationship.
Conclusion
A severe medical ailment called gout frequently coexists with other catastrophic illnesses. While leading a healthy lifestyle may reduce the likelihood of future flare-ups, it might not be sufficient to cure the illness. Even those who consume a balanced diet might acquire the ailment, and not everyone who consumes meals high in purines experiences gout symptoms. Medication might lessen discomfort and lower the chance of future gout flare-ups. People can discuss their symptoms with a doctor and get guidance on possible lifestyle modifications that can help them.